Abstract
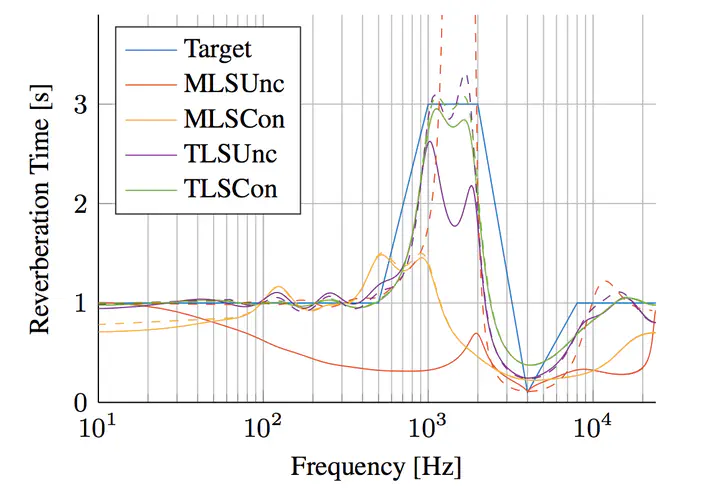
The reverberation time is one of the most prominent acoustical qualities of a physical room. Therefore, it is crucial that artificial reverberation algorithms match a specified target reverberation time accurately. In feedback delay networks, a popular framework for modeling room acoustics, the reverberation time is determined by combining delay and attenuation filters such that the frequency-dependent attenuation response is proportional to the delay length and by this complying to a global attenuation-per-second. However, only few details are available on the attenuation filter design as the approximation errors of the filter design are often regarded negligible. In this work, we demonstrate that the error of the filter approximation propagates in a non-linear fashion to the resulting reverberation time possibly causing large deviation from the specified target. For the special case of a proportional graphic equalizer, we propose a non-linear least squares solution and demonstrate the improved accuracy with a Monte Carlo simulation.